Payloads: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
(ADLO is obsolete. Various smaller fixes. GNUFI has been dead for ages. Remove duplicate entries. History should only contain history, not random payload info (that's partly duplicated).) |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
==== SeaBIOS ==== | ==== SeaBIOS ==== | ||
[[SeaBIOS]] is an open-source implementation of the standard bootstrap callback layer implemented by an x86 | [[SeaBIOS]] is an open-source implementation of the standard bootstrap callback layer implemented by an x86 BIOS. It enables booting from unmodified CDROMs and hard drives. | ||
SeaBIOS has been tested with Linux, NetBSD, FreeDOS, and Windows XP/Vista/7. Classic GRUB, lilo, and isolinux work well with SeaBIOS. | SeaBIOS has been tested with Linux, NetBSD, OpenBSD, FreeDOS, and Windows XP/Vista/7. Classic GRUB, lilo, and isolinux work well with SeaBIOS. Other x86 bootloaders and operating systems will likely also work. | ||
==== Official GRUB 2 ==== | ==== Official GRUB 2 ==== | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
An old version of [[GRUB2]] with coreboot and crypto support. | An old version of [[GRUB2]] with coreboot and crypto support. | ||
==== FILO ==== | ==== FILO ==== | ||
| Line 27: | Line 25: | ||
[[FILO]] is a simple bootloader with filesystem support. | [[FILO]] is a simple bootloader with filesystem support. | ||
==== Etherboot ==== | ==== Etherboot / GPXE ==== | ||
[[Etherboot]] is a network bootloader. It provides a direct replacement for proprietary PXE ROMs, with many extra features such as DNS, HTTP, iSCSI, etc. | [[Etherboot]] is a network bootloader. It provides a direct replacement for proprietary PXE ROMs, with many extra features such as DNS, HTTP, iSCSI, etc. | ||
| Line 33: | Line 31: | ||
Older versions of Etherboot included parts of [[FILO]], and thus supported SATA and USB booting. | Older versions of Etherboot included parts of [[FILO]], and thus supported SATA and USB booting. | ||
The new [[GPXE]] is not yet supported directly, various code changes are required before it can work as a coreboot payload. | The new [[GPXE]] is not yet supported directly, various code changes are required before it can work as a coreboot payload. However, GPXE works well when run with [[SeaBIOS]]. | ||
==== Open Firmware ==== | ==== Open Firmware ==== | ||
| Line 55: | Line 53: | ||
==== Linux ==== | ==== Linux ==== | ||
coreboot can use a [http://www.kernel.org Linux] kernel as payload directly. That is, the kernel is included in the ROM chip where coreboot resides. | |||
Alternatively, you can also boot a Linux kernel from your hard drive using either the [[FILO]], [[GRUB2]], or [[SeaBIOS]] payloads. | Alternatively, you can also boot a Linux kernel from your hard drive using either the [[FILO]], [[GRUB2]], or [[SeaBIOS]] payloads. | ||
| Line 61: | Line 59: | ||
==== FreeBSD ==== | ==== FreeBSD ==== | ||
[[Booting FreeBSD using coreboot|FreeBSD]] can be booted via coreboot | [[Booting FreeBSD using coreboot|FreeBSD]] can be booted via coreboot using [[SeaBIOS]]. | ||
==== OpenBSD ==== | ==== OpenBSD ==== | ||
[http://openbsd.org/ OpenBSD] can also be booted via coreboot | [http://openbsd.org/ OpenBSD] can also be booted via coreboot using [[SeaBIOS]]. | ||
This use-case is not well-tested yet, though. | This use-case is not well-tested yet, though. | ||
| Line 74: | Line 72: | ||
[[User:Jakllsch|jakllsch]] has worked on a partially-complete port of the x86 boot code to the role of native payload. However, with the advent of [[SeaBIOS]], this is likely to become less of a priority. Consult [[Coreboot and NetBSD]] for further information. | [[User:Jakllsch|jakllsch]] has worked on a partially-complete port of the x86 boot code to the role of native payload. However, with the advent of [[SeaBIOS]], this is likely to become less of a priority. Consult [[Coreboot and NetBSD]] for further information. | ||
==== FreeDOS ==== | |||
[[FreeDOS]] can be booted via coreboot using [[SeaBIOS]]. | |||
==== Windows ==== | ==== Windows ==== | ||
| Line 83: | Line 85: | ||
==== OpenSolaris ==== | ==== OpenSolaris ==== | ||
[[OpenSolaris]] has multiboot compliant kernels, and so it is possible to boot it with GRUB2 (pending some bug fixes). | [[OpenSolaris]] has multiboot compliant kernels, and so it is possible to boot it with [[GRUB2]] (pending some bug fixes). | ||
Some Sun engineers even worked on it, see http://bugs.opensolaris.org/bugdatabase/view_bug.do?bug_id=6475349 for information. | Some Sun engineers even worked on it, see [http://bugs.opensolaris.org/bugdatabase/view_bug.do?bug_id=6475349 this article] for more information. | ||
Currently, GRUB2 refuses to load the kernel due to a small bug in the multiboot header of the kernel, but the kernel still refuses to | Currently, GRUB2 refuses to load the kernel due to a small bug in the multiboot header of the kernel, but the kernel still refuses to work if that is worked around. Maybe they reintroduced some BIOS calls again? | ||
work if that is worked around. Maybe they reintroduced some BIOS calls again? | |||
See also [http://blogs.sun.com/szhou/entry/booting_solaris_from_linuxbios this blog entry]. | See also [http://blogs.sun.com/szhou/entry/booting_solaris_from_linuxbios this blog entry]. | ||
| Line 100: | Line 101: | ||
It can be run from within GRUB, but also as a coreboot payload (i.e. included in your ROM chip). | It can be run from within GRUB, but also as a coreboot payload (i.e. included in your ROM chip). | ||
'''Note:''' Current versions of memtest86 may not work anymore due to changes in coreboot. A patch is being worked on. | |||
<br clear="all" /> | <br clear="all" /> | ||
| Line 105: | Line 108: | ||
==== ADLO ==== | ==== ADLO ==== | ||
[[ADLO]] — Glue layer to 16-bit Bochs BIOS. Allows [[Booting Windows using coreboot|booting Windows]] and [http://openbsd.org/ OpenBSD]. | [[ADLO]] — Glue layer to 16-bit Bochs BIOS. Allows [[Booting Windows using coreboot|booting Windows]] and [http://openbsd.org/ OpenBSD]. | ||
'''Note:''' ADLO has been superseded by [[SeaBIOS]]. Do not use it anymore. | |||
==== Libpayload ==== | ==== Libpayload ==== | ||
| Line 121: | Line 126: | ||
[[Image:Bayou-screenshot-menu.jpg|160px|right]] | [[Image:Bayou-screenshot-menu.jpg|160px|right]] | ||
[[Bayou]] is the working name for a coreboot payload that can choose, load and run other payloads from a LAR archive on the ROM. | [[Bayou]] is the working name for a coreboot payload that can choose, load and run other payloads from a LAR archive on the ROM. | ||
'''Note:''' Bayou may no longer be in a working state right now, it may or may not be fixed and worked on again. In the meantime, [[SeaBIOS]] also provides a mechanism to include multiple payloads in a ROM image and select either of them at boot-time. | |||
<br clear="all" /> | <br clear="all" /> | ||
| Line 129: | Line 136: | ||
[[Image:Coreboot invaders.png|160px|right]] | [[Image:Coreboot invaders.png|160px|right]] | ||
[[GRUB invaders]] multi-boot compliant ''space invaders'' game. | [[GRUB invaders]] is a multi-boot compliant ''space invaders'' game. | ||
It can either be started from within GRUB (as a "kernel"), or it can be used as a coreboot payload. | It can either be started from within GRUB (as a "kernel"), or it can be used as a coreboot payload. | ||
| Line 146: | Line 153: | ||
* CodeGen's [http://www.openbios.org/SmartFirmware SmartFirmware] — IEEE1275-1994 Open Firmware | * CodeGen's [http://www.openbios.org/SmartFirmware SmartFirmware] — IEEE1275-1994 Open Firmware | ||
* [[Plan 9]] — A distributed operating system. | * [[Plan 9]] — A distributed operating system. | ||
* [[RedBoot]] / eCos — Real-time OS for embedded systems; initial port to ELF completed but no longer available. | * [[RedBoot]] / eCos — Real-time OS for embedded systems; initial port to ELF completed but no longer available. | ||
* HelenOS | * HelenOS | ||
* [http://www.reactos.org/ ReactOS] | * [http://www.reactos.org/ ReactOS] | ||
* DragonflyBSD | * DragonflyBSD | ||
* MirBSD | * MirBSD | ||
* MidnightBSD | * MidnightBSD | ||
* FreeRTOS | * FreeRTOS | ||
* QNX | * QNX | ||
| Line 169: | Line 172: | ||
== History == | == History == | ||
The payload was originally intended to be a Linux kernel stored in flash. Flash ROM growth rate was anticipated optimistically however, today there are not many mainboards that actually have enough flash ROM room for a kernel. 512KB can be seen here-and-there and a few boards come with 1MB. Recent kernels really want | The '''payload''' was originally intended to be a Linux kernel stored in flash. Flash ROM growth rate was anticipated optimistically however, and today there are not many mainboards that actually have enough flash ROM room for a kernel. 512KB can be seen here-and-there and a few boards come with 1MB or 2MB. Recent kernels really want at least 1MB, and then you'll only have room for 300-400 KB of initial ramdisk, which could be too small too, depending on the application. | ||
you'll only have room for 300-400 KB of initial ramdisk, which could be too small too, depending on the application | |||
So, other payloads are used; the two major ones are [[FILO]] and [[SeaBIOS]]. Also have a look at [[GRUB2]] and [[Etherboot]] (soon to be deprecated in favor of [[GPXE]]). | |||
Revision as of 01:26, 19 September 2010
coreboot in itself is "only" minimal code for initializing a mainboard with peripherals. After the initialization, it jumps to a payload.
Payloads
Bootloaders
SeaBIOS
SeaBIOS is an open-source implementation of the standard bootstrap callback layer implemented by an x86 BIOS. It enables booting from unmodified CDROMs and hard drives.
SeaBIOS has been tested with Linux, NetBSD, OpenBSD, FreeDOS, and Windows XP/Vista/7. Classic GRUB, lilo, and isolinux work well with SeaBIOS. Other x86 bootloaders and operating systems will likely also work.
Official GRUB 2
GRUB 2 is the official version 2 of GNU GRUB.
You can use the official GRUB 2 as a coreboot payload, in order to boot and operating system from a hard drive, for instance.
GRUB2
An old version of GRUB2 with coreboot and crypto support.
FILO
FILO is a simple bootloader with filesystem support.
Etherboot / GPXE
Etherboot is a network bootloader. It provides a direct replacement for proprietary PXE ROMs, with many extra features such as DNS, HTTP, iSCSI, etc.
Older versions of Etherboot included parts of FILO, and thus supported SATA and USB booting.
The new GPXE is not yet supported directly, various code changes are required before it can work as a coreboot payload. However, GPXE works well when run with SeaBIOS.
Open Firmware
Mitch Bradley's Open Firmware, an IEEE1275-1994 Open Firmware implementation, can also be used as coreboot payload.
OpenBIOS
OpenBIOS — IEEE1275-1994 Open Firmware.
Tiano Core
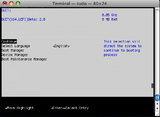
TianoCore is a bootloader providing the UEFI interface. See http://www.tianocore.org/ for more information.
Operating systems
Linux
coreboot can use a Linux kernel as payload directly. That is, the kernel is included in the ROM chip where coreboot resides.
Alternatively, you can also boot a Linux kernel from your hard drive using either the FILO, GRUB2, or SeaBIOS payloads.
FreeBSD
FreeBSD can be booted via coreboot using SeaBIOS.
OpenBSD
OpenBSD can also be booted via coreboot using SeaBIOS.
This use-case is not well-tested yet, though.
NetBSD
NetBSD/x86 boot code is known to work with SeaBIOS.
jakllsch has worked on a partially-complete port of the x86 boot code to the role of native payload. However, with the advent of SeaBIOS, this is likely to become less of a priority. Consult Coreboot and NetBSD for further information.
FreeDOS
FreeDOS can be booted via coreboot using SeaBIOS.
Windows
Windows can be booted with the help of SeaBIOS.
We have successfully booted Windows XP, Windows Vista and Windows 7 (Beta).
OpenSolaris
OpenSolaris has multiboot compliant kernels, and so it is possible to boot it with GRUB2 (pending some bug fixes). Some Sun engineers even worked on it, see this article for more information.
Currently, GRUB2 refuses to load the kernel due to a small bug in the multiboot header of the kernel, but the kernel still refuses to work if that is worked around. Maybe they reintroduced some BIOS calls again?
See also this blog entry.
Other
Memtest86 / Memtest86+
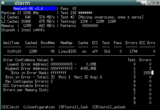
Memtest86 is a program which checks your RAM modules.
It can be run from within GRUB, but also as a coreboot payload (i.e. included in your ROM chip).
Note: Current versions of memtest86 may not work anymore due to changes in coreboot. A patch is being worked on.
ADLO
ADLO — Glue layer to 16-bit Bochs BIOS. Allows booting Windows and OpenBSD.
Note: ADLO has been superseded by SeaBIOS. Do not use it anymore.
Libpayload
Libpayload is a helper-library for payload-writers.
Coreinfo
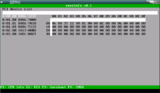
coreinfo is a coreboot payload which can display various system information.
Bayou
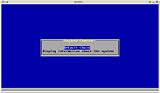
Bayou is the working name for a coreboot payload that can choose, load and run other payloads from a LAR archive on the ROM.
Note: Bayou may no longer be in a working state right now, it may or may not be fixed and worked on again. In the meantime, SeaBIOS also provides a mechanism to include multiple payloads in a ROM image and select either of them at boot-time.
Games
GRUB invaders
GRUB invaders is a multi-boot compliant space invaders game.
It can either be started from within GRUB (as a "kernel"), or it can be used as a coreboot payload.
TINT
tint is a falling blocks game.
Possible future payloads
The following payloads might or might not work (with more or less changes required) with coreboot — their usage hasn't been tested or documented so far.
- CodeGen's SmartFirmware — IEEE1275-1994 Open Firmware
- Plan 9 — A distributed operating system.
- RedBoot / eCos — Real-time OS for embedded systems; initial port to ELF completed but no longer available.
- HelenOS
- ReactOS
- DragonflyBSD
- MirBSD
- MidnightBSD
- FreeRTOS
- QNX
- Windows CE
- Haiku
- NanoVM (small JVM)
- uip / lwip (small TCP/IP stacks)
- MenuetOS
- KolibriOS
- Minix
History
The payload was originally intended to be a Linux kernel stored in flash. Flash ROM growth rate was anticipated optimistically however, and today there are not many mainboards that actually have enough flash ROM room for a kernel. 512KB can be seen here-and-there and a few boards come with 1MB or 2MB. Recent kernels really want at least 1MB, and then you'll only have room for 300-400 KB of initial ramdisk, which could be too small too, depending on the application.
So, other payloads are used; the two major ones are FILO and SeaBIOS. Also have a look at GRUB2 and Etherboot (soon to be deprecated in favor of GPXE).