The wiki is being retired! Documentation is now handled by the same processes we use for code: Add something to the Documentation/ directory in the coreboot repo, and it will be rendered to https://doc.coreboot.org/ . Contributions welcome!
coreboot (formerly known as LinuxBIOS) is a Free Software project aimed at replacing the proprietary BIOS (firmware) you can find in most of today's computers.
It performs just a little bit of hardware initialization and then executes a so-called payload , for example a Linux kernel, FILO , GRUB2 , OpenBIOS , Open Firmware , SmartFirmware , GNUFI (UEFI), Etherboot , ADLO (for booting Windows , FreeBSD , or OpenBSD ), Plan 9 , or memtest86 .
Benefits There are many reasons for using coreboot.
100% Free Software (GPL), no royalties, no license fees!
Fast boot times (3 seconds from power-on to Linux console)
Avoids the need for a slow, buggy, proprietary BIOS
Runs in 32-Bit protected mode almost from the start
Written in C, contains virtually no assembly code
Supports a wide variety of mainboards , devices , and payloads
Further features: netboot, serial console, remote flashing, ...
Use Cases coreboot can be deployed in a wide range of scenarios.
Standard desktop computers and servers
Clusters , high-performance computingSet-Top-Boxes, thin clients
Embedded solutions, appliances, terminals
Small form factor computers , Home-theater PCs (HTPC)No-moving-parts solutions (ROM chip as "hard drive")
Various non-standard scenarios (e.g. FPGA in Opteron socket)
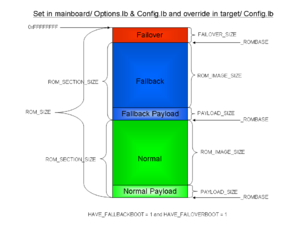
coreboot anatomy.
News
Contact